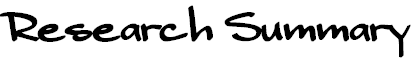The major research topics in these five years are
- development new catalytic asymmetric reactions by the use of organic catalysis
- development and application of high pressure induced by water-freezing to the organic synthesis
- total synthesis of biologically interesting molecules
which will be disclosed below.
1) Development new catalytic asymmetric reactions by the use of organic catalysis
The catalytic asymmetric reaction is one of the important topics in modern
organic synthesis. I have found the following two highly enantioselective
reactions using easily available proline-catalyst.
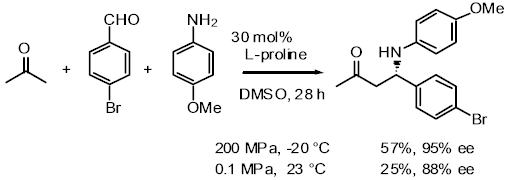
The direct and enantioselective, one-pot, three-component cross-Mannich
reaction of aldehydes:
The direct and diastereo- and enantio-selective, one-pot, three-component
cross-Mannich reaction of two different aldehydes has been developed, in
which one aldehyde is employed as the Mannich donor, and the other aldehyde
is utilized as a component of the Mannich acceptor, affording a b-aminoaldehyde
in a highly syn-diastereo- and enantio-selective manner.
The direct proline catalyzed asymmetric a-aminoxylation of aldehydes and ketones:
Aldehydes and ketones are reacted with nitrosobenzene in the presence
of a catalytic amount of proline, affording a-aminoxylated aldehydes and
ketones in good yield with high enantioselectivity, which are easily converted
into synthetically important a-hydroxy aldehydes and ketones.
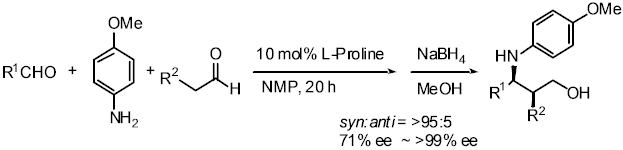
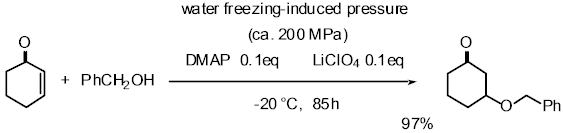
2) Development and application of high pressure induced by water-freezing
to the organic synthesis
Pressure is one important factor affecting the rate of organic reactions
and many reactions with a large, negative volume of activation have been
accelerated using high pressure. The volume of water increases about 10%
on freezing. When water is frozen in a sealed autoclave, a high pressure
of up to about 200 MPa can be realized. We have applied this high pressure
method to several reactions such as the Michael reaction of alcohols with
a,b-enones, and the Baylis-Hillmann reaction, proline-catalyzed Mannich
reaction of ketone, and proline-catalyzed aldol reaction. Especially in
the proline-mediated Mannich reaction under the high pressure induced by
water-freezing, Mannich adducts were obtained in better yield and higher
enantioselectivity than the reaction under normal pressure.
3) Total synthesis of biologically important molecule
There are many natural products which have interesting biological properties,
but their biological studies can not be developed because of the shortage
of supply from the natural sources. Chemical synthesis is one of the methods
for the production of these natural products. I have been engaged in the
total synthesis of such rare compounds with unique and complicated structures
based on the highly original methodology.
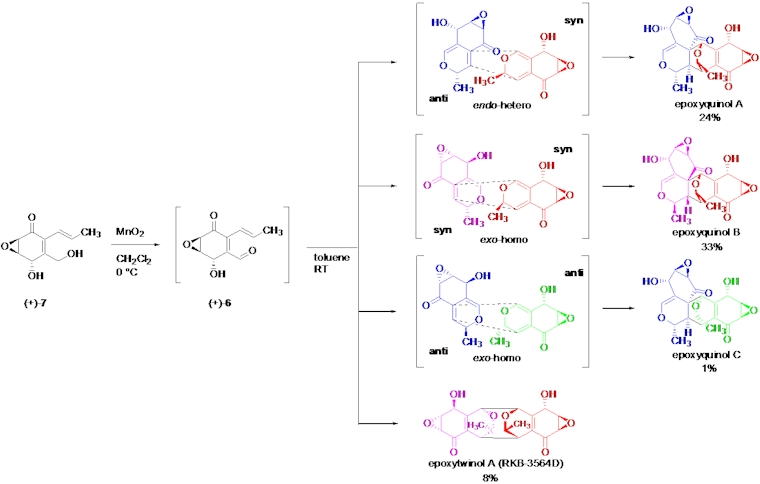
Angiogenesis inhibitors are promising drugs for the treatment of angiogenesis-related
diseases including cancer. Epoxyquinols A and B are unique pentaketide
dimers which show anti-angiogenic activity. Though structurally epoxyquinols
A and B have a highly functionalized and complicated heptacyclic ring system
containing 12 stereo-centers, biosynthetically it is proposed they are
formed via an unusual oxidative dimerization of the much simpler epoxycyclohexenone.
We have developed the first total synthesis of the naturally-occurring
enantiomers of (+)-epoxyquinols A and B using the postulated biomimetic
oxidative dimerization, along with determination of their absolute stereochemistry.
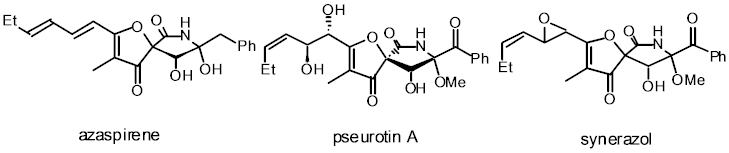
Azaspirene is a new angiogenesis inhibitors, containing a highly oxygenated 1-oxa-7-azaspiro[4.4]non-2-ene-4,6-dione skeleton with benzyl and hexadiene substituents. I have accomplished the first total synthesis of (-)-azaspirene, establishing its absolute stereochemistry. The key steps are a MgBr2•OEt2-mediated, diastereoselective Mukaiyama aldol reaction, a NaH-promoted, intramolecular cyclization of an alkynylamide, and the aldol reaction of a ketone containing functionalized g-lactam moiety without protection of tert-alcohol and amide functionalities. We has also synthesized pseurotin A for the first time by the similar methodology.
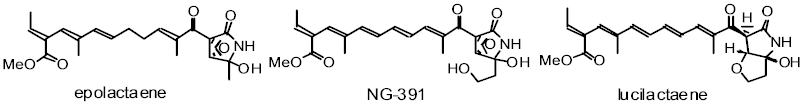
Epolactaene is a microbial metabolite, which is effective in promoting
neurite outgrowth and arresting the cell cycle at the G1 phase in a human
neuroblastoma cell line, so that it is regarded as a potential treatment
for various neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia. We have accomplished
a stereocontrolled total synthesis of both enantiomers of (+)- and (-)-epolactaene
from tetrahydropyran-2-ol. Key reactions are as follows: 1) The stereoselective
construction of the conjugated (E,E,E)-triene by a combination of kinetic
deprotonation and thermodynamic equilibration. 2) The (E)-selective Knoevenagel
condensation of b-ketonitrile with a chiral 2-alkoxyaldehyde. 3) A diastereoselective
epoxidation achieved using a bulky nucleophile (TrOOLi) and an appropriate
protecting group. 4) The mild hydrolysis of an a-epoxy nitrile by silica
gel on TLC facilitated by hydroxyl-mediated, intramolecular assistance.
We have also synthesized NG-391 which shows neurotrophic activity and an
effect on neurite outgrowth by our original methodology.
|